 |
SLProject 4.0.000
|
 |
SLProject 4.0.000
|
An SLMesh object is a triangulated mesh that is drawn with one draw call. More...
#include <SLMesh.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| SLMesh (SLAssetManager *assetMgr, const SLstring &name="Mesh") | |
| ~SLMesh () override | |
| The destructor deletes everything by calling deleteData. More... | |
| virtual void | init (SLNode *node) |
| SLMesh::shapeInit sets the transparency flag of the AABB. More... | |
| virtual void | draw (SLSceneView *sv, SLNode *node) |
| void | drawIntoDepthBuffer (SLSceneView *sv, SLNode *node, SLMaterial *depthMat) |
| Simplified drawing method for shadow map creation. More... | |
| void | addStats (SLNodeStats &stats) |
| virtual void | buildAABB (SLAABBox &aabb, const SLMat4f &wmNode) |
| void | updateAccelStruct () |
| SLbool | hit (SLRay *ray, SLNode *node) |
| virtual void | preShade (SLRay *ray) |
| virtual void | deleteData () |
| SLMesh::deleteData deletes all mesh data and vbo's. More... | |
| virtual void | deleteDataGpu () |
| void | deleteSelected (SLNode *node) |
| Deletes the rectangle selected vertices and the dependent triangles. More... | |
| void | deleteUnused () |
| Deletes unused vertices (= vertices that are not indexed in I16 or I32) More... | |
| virtual void | calcMinMax () |
| virtual void | calcNormals () |
| SLMesh::calcNormals recalculates vertex normals for triangle meshes. More... | |
| void | calcCenterRad (SLVec3f ¢er, SLfloat &radius) |
| SLbool | hitTriangleOS (SLRay *ray, SLNode *node, SLuint iT) |
| virtual void | generateVAO (SLGLVertexArray &vao) |
| Generate the Vertex Array Object for a specific shader program. More... | |
| void | computeHardEdgesIndices (float angleRAD, float epsilon) |
| computes the hard edges and stores the vertex indexes separately More... | |
| void | transformSkin (const std::function< void(SLMesh *)> &cbInformNodes) |
| Transforms the vertex positions and normals with by joint weights. More... | |
| void | deselectPartialSelection () |
| SLMaterial * | mat () const |
| SLMaterial * | matOut () const |
| SLGLPrimitiveType | primitive () const |
| const SLAnimSkeleton * | skeleton () const |
| SLuint | numI () const |
| SLGLVertexArray & | vao () |
| SLbool | isSelected () const |
| SLfloat | edgeAngleDEG () const |
| SLfloat | edgeWidth () const |
| SLCol4f | edgeColor () const |
| SLVec3f | finalP (SLuint i) |
| SLVec3f | finalN (SLuint i) |
| SLbool | accelStructIsOutOfDate () |
| void | mat (SLMaterial *m) |
| void | matOut (SLMaterial *m) |
| void | primitive (SLGLPrimitiveType pt) |
| void | skeleton (SLAnimSkeleton *skel) |
| void | isSelected (bool isSelected) |
| void | edgeWidth (SLfloat ew) |
| void | edgeAngleDEG (SLfloat ea) |
| void | edgeColor (const SLCol4f &ec) |
| void | vertexPosEpsilon (SLfloat eps) |
 Public Member Functions inherited from SLObject Public Member Functions inherited from SLObject | |
| SLObject (const SLstring &Name="", const SLstring &url="") | |
| virtual | ~SLObject () |
| void | name (const SLstring &Name) |
| void | url (const SLstring &url) |
| const SLstring & | name () const |
| const SLstring & | url () const |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static void | calcTex3DMatrix (SLNode *node) |
Public Attributes | |
| SLVVec3f | P |
| Vector for vertex positions layout (location = 0) More... | |
| SLVVec3f | N |
| Vector for vertex normals (opt.) layout (location = 1) More... | |
| SLVVec2f | UV [2] |
| Array of 2 Vectors for tex. coords. (opt.) layout (location = 2) More... | |
| SLVCol4f | C |
| Vector of vertex colors (opt.) layout (location = 4) More... | |
| SLVVec4f | T |
| Vector of vertex tangents (opt.) layout (location = 5) More... | |
| SLVVuchar | Ji |
| 2D Vector of per vertex joint ids (opt.) layout (location = 6) More... | |
| SLVVfloat | Jw |
| 2D Vector of per vertex joint weights (opt.) layout (location = 7) More... | |
| SLVVec3f | skinnedP |
| temp. vector for CPU skinned vertex positions More... | |
| SLVVec3f | skinnedN |
| temp. vector for CPU skinned vertex normals More... | |
| SLVushort | I16 |
| Vector of vertex indices 16 bit. More... | |
| SLVuint | I32 |
| Vector of vertex indices 32 bit. More... | |
| SLVuint | IS32 |
| Vector of rectangle selected vertex indices 32 bit. More... | |
| SLVushort | IE16 |
| Vector of hard edges vertex indices 16 bit (see computeHardEdgesIndices) More... | |
| SLVuint | IE32 |
| Vector of hard edges vertex indices 32 bit (see computeHardEdgesIndices) More... | |
| SLVec3f | minP |
| min. vertex in OS More... | |
| SLVec3f | maxP |
| max. vertex in OS More... | |
Protected Attributes | |
| SLGLPrimitiveType | _primitive |
| Primitive type (default triangles) More... | |
| SLMaterial * | _mat |
| Pointer to the inside material. More... | |
| SLMaterial * | _matOut |
| Pointer to the outside material. More... | |
| SLGLVertexArray | _vao |
| Main OpenGL Vertex Array Object for drawing. More... | |
| SLGLVertexArrayExt | _vaoN |
| OpenGL VAO for optional normal drawing. More... | |
| SLGLVertexArrayExt | _vaoT |
| OpenGL VAO for optional tangent drawing. More... | |
| SLGLVertexArrayExt | _vaoS |
| OpenGL VAO for optional selection drawing. More... | |
| SLbool | _isSelected |
| Flag if mesh is partially of fully selected. More... | |
| SLfloat | _edgeAngleDEG |
| Edge crease angle in degrees between face normals (30 deg. default) More... | |
| SLfloat | _edgeWidth |
| Line width for hard edge drawing. More... | |
| SLCol4f | _edgeColor |
| Color for hard edge drawing. More... | |
| SLfloat | _vertexPosEpsilon |
| Vertex position epsilon used in computeHardEdgesIndices. More... | |
| SLbool | _isVolume |
| Flag for RT if mesh is a closed volume. More... | |
| SLAccelStruct * | _accelStruct |
| KD-tree or uniform grid. More... | |
| SLbool | _accelStructIsOutOfDate |
| Flag id accel.struct needs update. More... | |
| SLAnimSkeleton * | _skeleton |
| The skeleton this mesh is bound to. More... | |
| SLVMat4f | _jointMatrices |
| Joint matrix vector for this mesh. More... | |
| SLVVec3f * | _finalP |
| Pointer to final vertex position vector. More... | |
| SLVVec3f * | _finalN |
| pointer to final vertex normal vector More... | |
 Protected Attributes inherited from SLObject Protected Attributes inherited from SLObject | |
| SLstring | _name |
| name of an object More... | |
| SLstring | _url |
| uniform resource locator More... | |
Private Member Functions | |
| void | calcTangents () |
| SLMesh::calcTangents computes the tangents per vertex for triangle meshes. More... | |
| void | drawSelectedVertices () |
| void | handleRectangleSelection (SLSceneView *sv, SLGLState *stateGL, SLNode *node) |
| Handles the rectangle section of mesh vertices (partial selection) More... | |
An SLMesh object is a triangulated mesh that is drawn with one draw call.
The SLMesh class represents a single mesh object. The mesh object is drawn with one draw call using the vertex indices in I16 or I32. A mesh can be drawn with triangles, lines or points. The vertex attributes are stored in vectors with equal number of elements:
P (vertex position, mandatory)
N (vertex normals)
C (vertex color)
UV[0] (1st. vertex texture coordinates) optional
UV[1] (2nd. vertex texture coordinates) optional
T (vertex tangents) optional
Ji (vertex joint index) optional 2D vector
Jw (vertex joint weights) optional 2D vector
I16 holds the unsigned short vertex indices.
I32 holds the unsigned int vertex indices.
The normals of a vertex are automatically calculated in the method calcNormals() by averaging the face normals of the adjacent triangles. A vertex has always only one normal and is used for the lighting calculation in the shader programs. With such averaged normals you can created a interpolated shading on smooth surfaces such as a sphere.
For objects with sharp edges such as a box you need 4 vertices per box face. All normals of a face point to the same direction. This means, that you have three times the same vertex position but with different normals for one corner of the box.
The following image shows a box with sharp edges and a sphere with mostly smooth but also 4 sharp edges. The smooth red normal as the top vertex got averaged because its position is only once in the vector P. On the other hand are the vertices of the hard edges in the front of the sphere doubled.
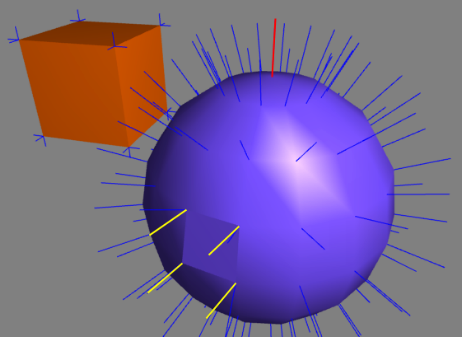
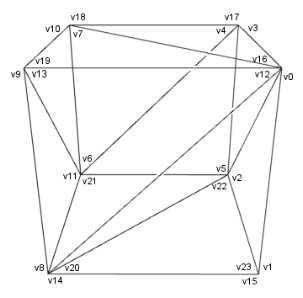
The following the example creates the box with 24 vertices:
The vertex positions and normals in P and N:
P.size = 24
P[0] = [1,1,1] N[0] = [1,0,0]
P[1] = [1,0,1] N[1] = [1,0,0]
P[2] = [1,0,0] N[2] = [1,0,0]
P[3] = [1,1,0] N[3] = [1,0,0]
P[4] = [1,1,0] N[4] = [0,0,-1]
P[5] = [1,0,0] N[5] = [0,0,-1]
P[6] = [0,0,0] N[6] = [0,0,-1]
P[7] = [0,1,0] N[7] = [0,0,-1]
P[8] = [0,0,1] N[8] = [-1,0,0]
P[9] = [0,1,1] N[9] = [-1,0,0]
P[10]= [0,1,0] N[10]= [-1,0,0]
P[11]= [0,0,0] N[11]= [-1,0,0]
P[12]= [1,1,1] N[12]= [0,0,1]
P[13]= [0,1,1] N[13]= [0,0,1]
P[14]= [0,0,1] N[14]= [0,0,1]
P[15]= [1,0,1] N[15]= [0,0,1]
P[16]= [1,1,1] N[16]= [0,1,0]
P[17]= [1,1,0] N[17]= [0,1,0]
P[18]= [0,1,0] N[18]= [0,1,0]
P[19]= [0,1,1] N[19]= [0,1,0]
P[20]= [0,0,0] N[20]= [0,-1,0]
P[21]= [1,0,0] N[21]= [0,-1,0]
P[22]= [1,0,1] N[22]= [0,-1,0]
P[23]= [0,0,1] N[23]= [0,-1,0]
The vertex indices in I16:
I16[] = {0,1,2, 0,2,3,
4,5,6, 4,6,7,
8,9,10, 8,10,11,
12,13,14, 12,14,15,
16,17,18, 16,18,19,
20,21,22, 20,22,23}
All vertex attributes are added to the vertex array object _vao (SLVertexArray).
All arrays remain in the main memory for ray tracing. A mesh uses only one material referenced by the SLMesh::mat pointer.
If a mesh is associated with a skeleton all its vertices and normals are transformed every frame by the joint weights. Every vertex of a mesh has weights for 1-n joints by which it can be influenced. This transform is called skinning and is done in CPU in the method transformSkin. The final transformed vertices and normals are stored in _finalP and _finalN.
|
explicit |
Constructor for mesh objects. Meshes can be used in multiple nodes (SLNode). Meshes can belong therefore to the global assets such as meshes (SLMesh), materials (SLMaterial), textures (SLGLTexture) and shader programs (SLGLProgram).
| assetMgr | Pointer to a global asset manager. If passed the asset manager is the owner of the instance and will do the deallocation. If a nullptr is passed the creator is responsible for the deallocation. |
| name | Name of the mesh |
|
override |
The destructor deletes everything by calling deleteData.
The destructor should be called by the owner of the mesh. If an asset manager was passed in the constructor it will do it after scene destruction. The material (SLMaterial) that the mesh uses will not be deallocated.
|
inline |
| void SLMesh::addStats | ( | SLNodeStats & | stats | ) |
SLMesh::updateStats updates the parent node statistics.
SLMesh::buildAABB builds the passed axis-aligned bounding box in OS and updates the min & max points in WS with the passed WM of the node.
Reimplemented in SLParticleSystem.
SLMesh::calcCenterRad calculates the center and the radius of an almost minimal bounding sphere. Code by Jack Ritter from Graphic Gems.
|
virtual |
SLMesh::calcMinMax calculates the axis alligned minimum and maximum point
|
virtual |
SLMesh::calcNormals recalculates vertex normals for triangle meshes.
SLMesh::calcNormals recalculates the normals only from the vertices. This algorithms doesn't know anything about smoothgroups. It just loops over the triangle of the material faces and sums up the normal for each of its vertices. Note that the face normals are not normalized. The cross product of 2 vectors is proportional to the area of the triangle. Like this the normal of big triangles are more weighted than small triangles and we get a better normal quality. At the end all vertex normals are normalized.
|
private |
SLMesh::calcTangents computes the tangents per vertex for triangle meshes.
SLMesh::calcTangents computes the tangent and bi-tangent per vertex used for GLSL normal map bump mapping. The code and mathematical derivation is in detail explained in: http://www.terathon.com/code/tangent.html
|
static |
| void SLMesh::computeHardEdgesIndices | ( | float | angleDEG, |
| float | epsilon | ||
| ) |
computes the hard edges and stores the vertex indexes separately
Hard edges are edges between faces where there normals have an angle greater than angleDEG (by default 30°). If a mesh has only smooth edges such as a sphere there will be no hard edges. The indices of those hard edges are stored in the vector IE16 or IE32. For rendering these indices are appended behind the indices for the triangle drawing. This is because the index the same vertices of the same VAO. See SLMesh::generateVAO for the details.
|
virtual |
SLMesh::deleteData deletes all mesh data and vbo's.
Reimplemented in SLParticleSystem.
|
virtual |
Reimplemented in SLParticleSystem.
| void SLMesh::deleteSelected | ( | SLNode * | node | ) |
Deletes the rectangle selected vertices and the dependent triangles.
The selection rectangle is defined in SLScene::selectRect and gets set and drawn in SLCamera::onMouseDown and SLCamera::onMouseMove. All vertices that are within the selectRect are listed in SLMesh::IS32. The selection evaluation is done during drawing in SLMesh::handleRectangleSelection and is only valid for the current frame. See also SLMesh::handleRectangleSelection.
| void SLMesh::deleteUnused | ( | ) |
Deletes unused vertices (= vertices that are not indexed in I16 or I32)
| void SLMesh::deselectPartialSelection | ( | ) |
Clears the partial selection but not the flag SLMesh::_isSelected See also SLMesh::handleRectangleSelection.
|
virtual |
SLMesh::draw does the OpenGL rendering of the mesh. The GL_TRIANGLES primitives are rendered normally with the vertex position vector P, the normal vector N, the vector UV1 and the index vector I16 or I32. GL_LINES & GL_POINTS don't have normals and tex.coords. GL_POINTS don't have indexes (I16,I32) and are rendered with glDrawArrays instead glDrawElements. Optionally you can draw the normals and/or the uniform grid voxels.
The method performs the following steps:
1) Apply the drawing bits
2) Generate Vertex Array Object once
3) Apply the uniform variables to the shader
3a) Activate a shader program if it is not yet in use and apply all its material parameters.
3b) Pass the standard matrices to the shader program.
4) Finally do the draw call by calling SLGLVertexArray::drawElementsAs
5) Draw optional normals & tangents
6) Draw optional acceleration structure
7) Draw selected mesh with points
Please view also the full process of rendering one frame
Reimplemented in SLParticleSystem.
| void SLMesh::drawIntoDepthBuffer | ( | SLSceneView * | sv, |
| SLNode * | node, | ||
| SLMaterial * | depthMat | ||
| ) |
Simplified drawing method for shadow map creation.
This is used from within SLShadowMap::drawNodesIntoDepthBufferRec
|
private |
If the entire mesh is selected all points will be drawn with an the vertex array only without indices. If a subset is selected we use the extra index array IS32. See also SLMesh::handleRectangleSelection.
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
virtual |
Generate the Vertex Array Object for a specific shader program.
|
private |
Handles the rectangle section of mesh vertices (partial selection)
SLMesh::hit does the ray-mesh intersection test. If no acceleration structure is defined all triangles are tested in a brute force manner.
SLMesh::hitTriangleOS is the fast and minimum storage ray-triangle intersection test by Tomas Moeller and Ben Trumbore (Journal of graphics tools 2, 1997).
|
virtual |
SLMesh::shapeInit sets the transparency flag of the AABB.
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
virtual |
SLMesh::preShade calculates the rest of the intersection information after the final hit point is determined. Should be called just before the shading when the final intersection point of the closest triangle was found.
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
| void SLMesh::transformSkin | ( | const std::function< void(SLMesh *)> & | cbInformNodes | ) |
Transforms the vertex positions and normals with by joint weights.
If the mesh is used for skinned skeleton animation this method transforms each vertex and normal by max. four joints of the skeleton. Each joint has a weight and an index. After the transform the VBO have to be updated. This skinning process can also be done (a lot faster) on the GPU. This software skinning is also needed for ray or path tracing.
| void SLMesh::updateAccelStruct | ( | ) |
SLMesh::updateAccelStruct rebuilds the acceleration structure if the dirty flag is set. This can happen for mesh animations.
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
protected |
KD-tree or uniform grid.
|
protected |
Flag id accel.struct needs update.
|
protected |
Edge crease angle in degrees between face normals (30 deg. default)
|
protected |
Color for hard edge drawing.
|
protected |
Line width for hard edge drawing.
|
protected |
pointer to final vertex normal vector
|
protected |
Pointer to final vertex position vector.
|
protected |
Flag if mesh is partially of fully selected.
|
protected |
Flag for RT if mesh is a closed volume.
|
protected |
Joint matrix vector for this mesh.
|
protected |
Pointer to the inside material.
|
protected |
Pointer to the outside material.
|
protected |
Primitive type (default triangles)
|
protected |
The skeleton this mesh is bound to.
|
protected |
Main OpenGL Vertex Array Object for drawing.
|
protected |
OpenGL VAO for optional normal drawing.
|
protected |
OpenGL VAO for optional selection drawing.
|
protected |
OpenGL VAO for optional tangent drawing.
|
protected |
Vertex position epsilon used in computeHardEdgesIndices.
| SLVCol4f SLMesh::C |
Vector of vertex colors (opt.) layout (location = 4)
| SLVushort SLMesh::I16 |
Vector of vertex indices 16 bit.
| SLVuint SLMesh::I32 |
Vector of vertex indices 32 bit.
| SLVushort SLMesh::IE16 |
Vector of hard edges vertex indices 16 bit (see computeHardEdgesIndices)
| SLVuint SLMesh::IE32 |
Vector of hard edges vertex indices 32 bit (see computeHardEdgesIndices)
| SLVuint SLMesh::IS32 |
Vector of rectangle selected vertex indices 32 bit.
| SLVVuchar SLMesh::Ji |
2D Vector of per vertex joint ids (opt.) layout (location = 6)
| SLVVfloat SLMesh::Jw |
2D Vector of per vertex joint weights (opt.) layout (location = 7)
| SLVec3f SLMesh::maxP |
max. vertex in OS
| SLVec3f SLMesh::minP |
min. vertex in OS
| SLVVec3f SLMesh::N |
Vector for vertex normals (opt.) layout (location = 1)
| SLVVec3f SLMesh::P |
Vector for vertex positions layout (location = 0)
| SLVVec3f SLMesh::skinnedN |
temp. vector for CPU skinned vertex normals
| SLVVec3f SLMesh::skinnedP |
temp. vector for CPU skinned vertex positions
| SLVVec4f SLMesh::T |
Vector of vertex tangents (opt.) layout (location = 5)
| SLVVec2f SLMesh::UV[2] |
Array of 2 Vectors for tex. coords. (opt.) layout (location = 2)